
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Healthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Large Prospective Cohort Study
- Qing Chang, Yixiao Zhang, Tingjing Zhang, Zuyun Liu, Limin Cao, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Shaomei Sun, Xing Wang, Ming Zhou, Qiyu Jia, Kun Song, Yang Ding, Yuhong Zhao, Kaijun Niu, Yang Xia
- Received April 27, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online March 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0133 [Epub ahead of print]
- 618 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
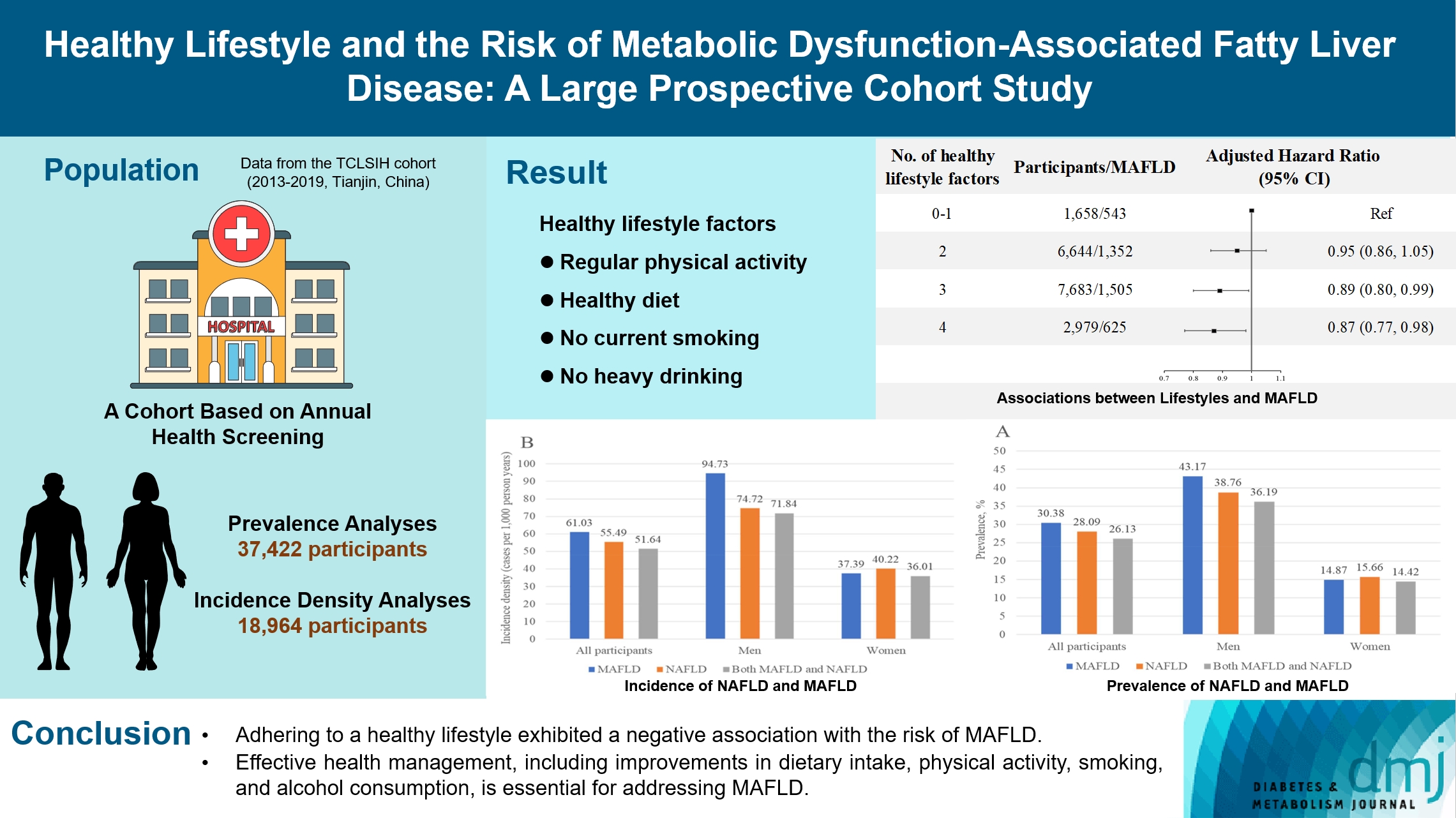
The incidence density of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and the effect of a healthy lifestyle on the risk of MAFLD remain unknown. We evaluated the prevalence and incidence density of MAFLD and investigated the association between healthy lifestyle and the risk of MAFLD.
Methods
A cross-sectional analysis was conducted on 37,422 participants to explore the prevalence of MAFLD. A cohort analysis of 18,964 individuals was conducted to identify the incidence of MAFLD, as well as the association between healthy lifestyle and MAFLD. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) with adjustments for confounding factors.
Results
The prevalence of MAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and their comorbidities were 30.38%, 28.09%, and 26.13%, respectively. After approximately 70 thousand person-years of follow-up, the incidence densities of the three conditions were 61.03, 55.49, and 51.64 per 1,000 person-years, respectively. Adherence to an overall healthy lifestyle was associated with a 19% decreased risk of MAFLD (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.72 to 0.92), and the effects were modified by baseline age, sex, and body mass index (BMI). Subgroup analyses revealed that younger participants, men, and those with a lower BMI experienced more significant beneficial effects from healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Our results highlight the beneficial effect of adherence to a healthy lifestyle on the prevention of MAFLD. Health management for improving dietary intake, physical activity, and smoking and drinking habits are critical to improving MAFLD.
- Basic Research
- Sulforaphane Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis through Epigenetic Up-Regulation of BMP-7
- Lili Kong, Hongyue Wang, Chenhao Li, Huiyan Cheng, Yan Cui, Li Liu, Ying Zhao
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):909-920. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0168
- 5,435 View
- 141 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
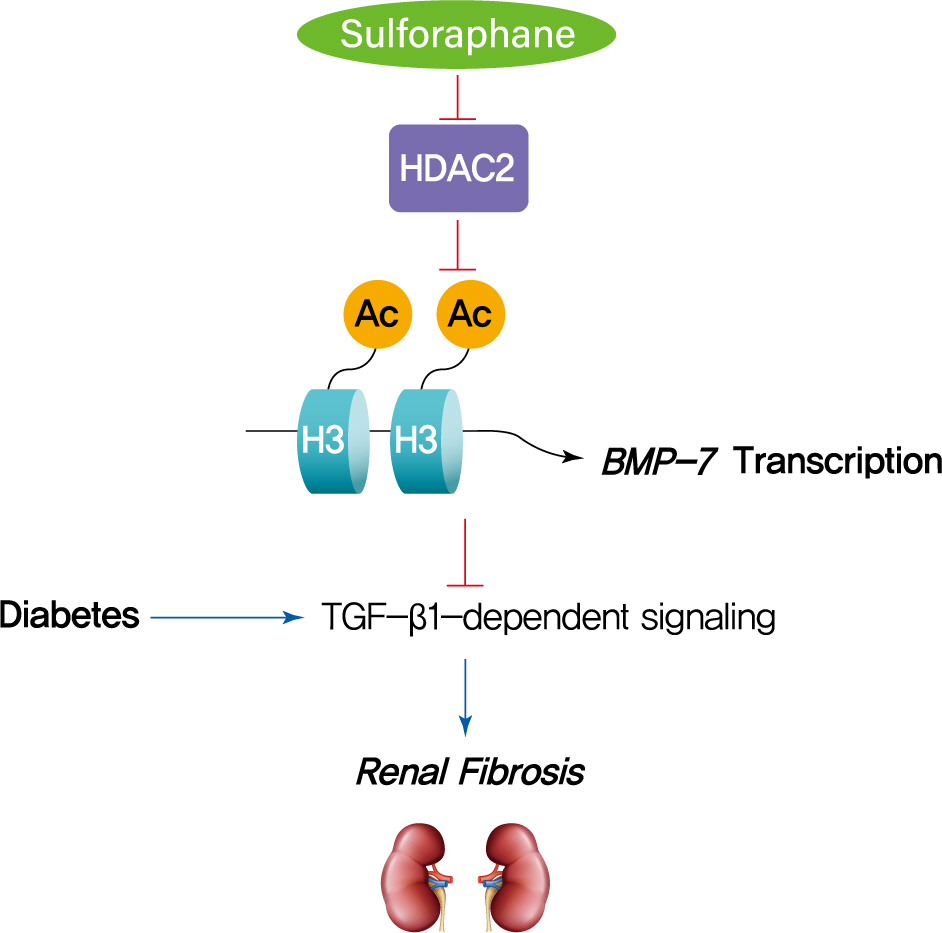
The dietary agent sulforaphane (SFN) has been reported to reduce diabetes-induced renal fibrosis, as well as inhibit histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. Bone morphologic protein 7 (BMP-7) has been shown to reduce renal fibrosis induced by transforming growth factor-beta1. The aim of this study was to investigate the epigenetic effect of SFN on BMP-7 expression in diabetes-induced renal fibrosis.
Methods
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice and age-matched controls were subcutaneously injected with SFN or vehicle for 4 months to measure the in vivo effects of SFN on the kidneys. The human renal proximal tubular (HK11) cell line was used to mimic diabetic conditions in vitro. HK11 cells were transfected to over-express HDAC2 and treated with high glucose/palmitate (HG/Pal) to explore the epigenetic modulation of BMP-7 in SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced renal fibrosis.
Results
SFN significantly attenuated diabetes-induced renal fibrosis in vivo. Among all of the HDACs we detected, HDAC2 activity was markedly elevated in the STZ-induced diabetic kidneys and HG/Pal-treated HK11 cells. SFN inhibited the diabetes-induced increase in HDAC2 activity which was associated with histone acetylation and transcriptional activation of the BMP-7 promoter. HDAC2 over-expression reduced BMP-7 expression and abolished the SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced fibrosis in vitro.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that the HDAC inhibitor SFN protects against diabetes-induced renal fibrosis through epigenetic up-regulation of BMP-7. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
Zhenzhen Zhang, Huali Chen, Cheng Pan, Rui Li, Wangsheng Zhao, Tianzeng Song
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119626. CrossRef - Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds in Preventing and Reversing Organ Fibrosis and the Underlying Mechanisms
Patrícia dos Santos Azeredo, Daping Fan, E. Angela Murphy, Wayne E. Carver
Cells.2024; 13(5): 421. CrossRef - Beneficial role of broccoli and its active ingredient, sulforaphane in the treatment of diabetes
Aminu Mohammed, Hafsat Abdullahi Mohammed
Phytomedicine Plus.2023; 3(2): 100431. CrossRef - The Role of Histone Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Christodoula Kourtidou, Konstantinos Tziomalos
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 6007. CrossRef - Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of NRF2 in Kidney Injury and Diseases
Da-Wei Lin, Yung-Chien Hsu, Cheng-Chih Chang, Ching-Chuan Hsieh, Chun-Liang Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6053. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Sulforaphane on Diabetes and Its Complications via Both Nrf2-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms
Minhyuk Kim, Joo Young Lee
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sulforaphane exhibits potent renoprotective effects in preclinical models of kidney diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Elisa B. Monteiro, Matheus Ajackson, Milena B. Stockler-Pinto, Fitsum Guebre-Egziabher, Julio B. Daleprane, Christophe O. Soulage
Life Sciences.2023; 322: 121664. CrossRef - Integrated single-cell RNA-seq analysis revealed podocyte injury through activation of the BMP7/AMPK/mTOR mediated autophagy pathway
Hongzhou Lin, Huihui Chen, Rengcheng Qian, Guoqi Tang, Yinjuan Ding, Yalan Jiang, Congde Chen, Dexuan Wang, Maoping Chu, Xiaoling Guo
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110559. CrossRef - Underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of genistein in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications
Tao Jiang, Yuhe Dong, Wanying Zhu, Tong Wu, Linyan Chen, Yuantong Cao, Xi Yu, Ye Peng, Ling Wang, Ying Xiao, Tian Zhong
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Sulforaphane: A nutraceutical against diabetes-related complications
Sinenhlanhla X.H. Mthembu, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Marakiya T. Moetlediwa, Ndivhuwo Muvhulawa, Sonia Silvestri, Patrick Orlando, Bongani B. Nkambule, Christo J.F. Muller, Duduzile Ndwandwe, Albertus K. Basson, Luca Tiano, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Pharmacological Research.2023; 196: 106918. CrossRef - Nrf2/HO-1 as a therapeutic target in renal fibrosis
Emad H.M. Hassanein, Islam M. Ibrahim, Esraa K. Abd-alhameed, Zeina W. Sharawi, Fatima A. Jaber, Hanan S. Althagafy
Life Sciences.2023; 334: 122209. CrossRef - A mechanistic overview of sulforaphane and its derivatives application in diabetes and its complications
Neda Mohamadi, Vafa Baradaran Rahimi, Mohammad Reza Fadaei, Fatemeh Sharifi, Vahid Reza Askari
Inflammopharmacology.2023; 31(6): 2885. CrossRef - The HDAC2/SP1/miR-205 feedback loop contributes to tubular epithelial cell extracellular matrix production in diabetic kidney disease
Zongji Zheng, Shuting Zhang, Jiaqi Chen, Meina Zou, Yanlin Yang, Wen Lu, Shijing Ren, Xiangyu Wang, Wenhui Dong, Zikun Zhang, Ling Wang, Meiping Guan, Gladys L.Y. Cheing, Yaoming Xue, Yijie Jia
Clinical Science.2022; 136(3): 223. CrossRef - BMP-7 Upregulates Id2 Through the MAPK Signaling Pathway to Improve Diabetic Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and the Intervention of Oxymatrine
Yawen Xiao, Dan Liang, Zhiyang Li, Zhaowei Feng, Zhiping Yuan, Fan Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Yuxia Zhou, Mingjun Shi, Lingling Liu, Ying Xiao, Bing Guo
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HDAC1 Promotes Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by
Inhibiting BMP-7 Transcription Through Histone Deacetylation
Chun Ouyang, Lei Huang, Xiaoqiang Ye, Mingming Ren, Zhen Han
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(10): 660. CrossRef - Class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition ameliorates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal tubular cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy and proliferation
Jialu Li, Chao Yu, Fengchen Shen, Binbin Cui, Na Liu, Shougang Zhuang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of histone deacetylases and inhibitors in renal fibrosis progression
Jiayu Wang, Jiaxing Li, Xin Zhang, Min Zhang, Xiaopeng Hu, Hang Yin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The improvement of sulforaphane in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and related complications: A review
Mengjiao Wang, Min Chen, Rui Guo, Yangyang Ding, Haihui Zhang, Yuanqing He
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2022; 129: 397. CrossRef - Defining therapeutic targets for renal fibrosis: Exploiting the biology of pathogenesis
Hao Yan, Jiangxin Xu, Zhifei Xu, Bo Yang, Peihua Luo, Qiaojun He
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 143: 112115. CrossRef
- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
- Improving Patients' Adherence to Physical Activity in Diabetes Mellitus: A Review
- Shan-hu Qiu, Zi-lin Sun, Xue Cai, Lili Liu, Bingquan Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(1):1-5. Published online February 17, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.1.1
- 4,284 View
- 51 Download
- 44 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Regular physical activity (PA) is a key element in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Participation in regular PA improves blood glucose control and can prevent or delay T2DM and its complications, along with positively affecting lipids, blood pressure, cardiovascular events, mortality, and quality of life. However, most people with T2DM are not active and show poor adherence. This paper reviews the possible barriers to PA and strategies to improve the adherence to PA. Based on the currently available literature, it is concluded that self-efficacy and social support from family, friends, and health care providers play the important role in adoption and maintenance of regular PA. Here we also highlight some new modern and innovative interventions that facilitate exercise participation and improve the adherence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with diabetes mellitus among adults: Findings from the Indonesian Family Life Survey-5
Mohammed Alfaqeeh, Sofa D. Alfian, Rizky Abdulah
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2024; 14: 100161. CrossRef - Barriers and Enablers for Physical Activity Engagement Among Individuals From India With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Mixed-Method Study
Prabhath Matpady, Arun G. Maiya, Pallavi P. Saraswat, Chythra R. Rao, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Shekarappa D. Anupama, Jeevan K. Shetty, Shashikiran Umakanth
Journal of Physical Activity and Health.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of physical activity promotion program on adherence to physical exercise among patients with type II diabetes in North Shoa Zone Amhara region: a quasi-experimental study
Akine Eshete, Sadat Mohammed, Sisay Shine, Yosef Eshetie, Yibeltal Assefa, Nigussie Tadesse
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A framework for incorporating physical activity in treatment: Competencies, guidelines, and implications for family therapists
Josh R. Novak, Faith K. Ellis
Journal of Marital and Family Therapy.2022; 48(2): 523. CrossRef - New insights into the role and therapeutic potential of HSP70 in diabetes
Amanda Almeida de Oliveira, Valentina Ochoa Mendoza, Swasti Rastogi, Kenia Pedrosa Nunes
Pharmacological Research.2022; 178: 106173. CrossRef - The bidirectional relationship between AMPK pathway activation and myokine secretion in skeletal muscle: How it affects energy metabolism
Mahdi Ahsan, Léa Garneau, Céline Aguer
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Community-Based Structured Physical Activity Program for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes
Aishee B. Mukherji, Di Lu, FeiFei Qin, Haley Hedlin, Neil M. Johannsen, Sukyung Chung, Yukari Kobayashi, Francois Haddad, Cynthia Lamendola, Marina Basina, Ruth Talamoa, Jonathan Myers, Latha Palaniappan
JAMA Network Open.2022; 5(12): e2247858. CrossRef - A correlational study to assess the level of perception and exercise barriers among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
ML Sarika, Srijita Chakraborty, Payel Panda
International Journal of Diabetes and Technology.2022; 1(2): 63. CrossRef - Recreational training improves cardiovascular adaptations, metabolic profile and mental health of elderly women with type-2 diabetes mellitus
Andrea Sanches, Vinicius Guzzoni, Vania C. dos R. Miranda, Laís Bonagurio Peressim, Suellen Rocha, Patrícia Oliveira de Lima, Fernanda Klein Marcondes, Ana Paula Tanno, Tatiana Sousa Cunha
Health Care for Women International.2021; 42(11): 1279. CrossRef - Serum fetuin‐A and Ser312 phosphorylated fetuin‐A responses and markers of insulin sensitivity after a single bout of moderate intensity exercise
Guang Ren, Robert L. Bowers, Teayoun Kim, Alonzo J. Mahurin, Peter W. Grandjean, Suresh T. Mathews
Physiological Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise as a Therapeutic Intervention in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Konstantina Dipla, Andreas Zafeiridis, Gesthimani Mintziori, Afroditi K. Boutou, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Anthony C. Hackney
Endocrines.2021; 2(2): 65. CrossRef - Feasibility of a home-based foot–ankle exercise programme for musculoskeletal dysfunctions in people with diabetes: randomised controlled FOotCAre (FOCA) Trial II
Érica Q. Silva, Danilo P. Santos, Raquel I. Beteli, Renan L. Monteiro, Jane S. S. P. Ferreira, Ronaldo H. Cruvinel-Junior, Asha Donini, Jady L. Verissímo, Eneida Y. Suda, Isabel C. N. Sacco
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Active Video Game Program for People with Type 2 Diabetes- a Pilot Study
Han-Hung Huang, Brianna Gathright, Rachel Holik, Hannah Iverson, Emily Saville, Drew A. Curtis
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(22): 11046. CrossRef - Feasibility and safety of a walking football program in middle-aged and older men with type 2 diabetes
Ana Barbosa, João Brito, Júlio Costa, Pedro Figueiredo, André Seabra, Romeu Mendes
Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 63(6): 786. CrossRef - Adherence to Medication, Diet and Physical Activity and the Associated Factors Amongst Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Alireza Mirahmadizadeh, Haniyeh Khorshidsavar, Mozhgan Seif, Mohammad Hossein Sharifi
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(2): 479. CrossRef - Malay Version of Exercise Self-Efficacy: A Confirmatory Analysis among Malaysians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Aizuddin Hidrus, Yee Cheng Kueh, Bachok Norsa’adah, Garry Kuan
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(3): 922. CrossRef - Motivation and Barriers to Maintaining Lifestyle Changes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes after an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention (The U-TURN Trial): A Longitudinal Qualitative Study
Sabrina K. Schmidt, Liv Hemmestad, Christopher S. MacDonald, Henning Langberg, Laura S. Valentiner
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7454. CrossRef - Understanding patients’ experience living with diabetes type 2 and effective disease management: a qualitative study following a mobile health intervention in Bangladesh
F. Yasmin, L. Ali, B. Banu, F. B. Rasul, R. Sauerborn, A. Souares
BMC Health Services Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility of procedures for a randomised pilot study of reduced exertion, high-intensity interval training (REHIT) with non-diabetic hyperglycaemia patients
Matthew Haines
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutritional Strategies to Combat Type 2 Diabetes in Aging Adults: The Importance of Protein
Kayleigh M. Beaudry, Michaela C. Devries
Frontiers in Nutrition.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic review of adherence to diabetes self‐care behaviours: Evidence from low‐ and middle‐income countries
Victor Mogre, Natalie A. Johnson, Flora Tzelepis, Jonathan E. Shaw, Christine Paul
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2019; 75(12): 3374. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes and physical activity: barriers and enablers to diabetes control in Eastern India
Pati Sanghamitra, Lobo Eunice, Pati Sandipana, Desaraju Shayma, Mahapatra Pranab
Primary Health Care Research & Development.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Utility of Self-Report Measures of Affect to Optimise Exercise Adherence in People with Type 2 Diabetes
Emily R. Cox, Shelley Elizabeth Keating, Jeff S. Coombes, Nicola W. Burton
Current Diabetes Reviews.2019; 15(4): 302. CrossRef - Mechanisms Involved in Glycemic Control Promoted by Exercise in Diabetics
Eric Francelino Andrade, Víviam de Oliveira Silva, Débora Ribeiro Orlando, Luciano José Pereira
Current Diabetes Reviews.2019; 15(2): 105. CrossRef - Equity of a government subsidised exercise referral scheme: A population study
Melinda Craike, Glen Wiesner, Joanne Enticott, Jason A. Bennie, Stuart J.H. Biddle
Social Science & Medicine.2018; 216: 20. CrossRef - Relating Activity and Participation Levels to Glycemic Control, Emergency Department Use, and Hospitalizations in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Matt P. Malcolm, Karen E. Atler, Arlene A. Schmid, Tara C. Klinedinst, Laura A. Grimm, Tasha P. Marchant, David R. Marchant
Clinical Diabetes.2018; 36(3): 232. CrossRef - How can clinical practices pragmatically increase physical activity for patients with type 2 diabetes? A systematic review
Kelsey A. Luoma, Ian M. Leavitt, Joel C. Marrs, Andrea L. Nederveld, Judith G. Regensteiner, Andrea L. Dunn, Russell E. Glasgow, Amy G. Huebschmann
Translational Behavioral Medicine.2017; 7(4): 751. CrossRef - Interleukin-6 increases the expression and activity of insulin-degrading enzyme
Mirian A. Kurauti, José M. Costa-Júnior, Sandra M. Ferreira, Gustavo J. Santos, Carlos H. G. Sponton, Everardo M. Carneiro, Guilherme D. Telles, Mara P. T. Chacon-Mikahil, Cláudia R. Cavaglieri, Luiz F. Rezende, Antonio C. Boschero
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Face-to-Face and Telephone-Based Family-Oriented Education on Self-Care Behavior and Patient Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Masumeh Hemmati Maslakpak, Somaieh Razmara, Zahra Niazkhani
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Beliefs about Genetically Targeted Care in African Americans
Chanita Hughes Halbert, Jasmine A. McDonald, Gayenell Magwood, Melanie Jefferson
Journal of the National Medical Association.2017; 109(2): 98. CrossRef - Mobile Exergaming for Health—Effects of a serious game application for smartphones on physical activity and exercise adherence in type 2 diabetes mellitus—study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Christoph Höchsmann, Steffen P. Walz, Juliane Schäfer, Jussi Holopainen, Henner Hanssen, Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss
Trials.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of glucose dynamics by noninvasive peripheral electrical stimulation in normal and insulin-resistant rats
Merav Catalogna, Sigal Fishman, Zamir Halpern, Shani Ben-Shlomo, Uri Nevo, Eshel Ben-Jacob
Metabolism.2016; 65(6): 863. CrossRef - Effects of Exergaming on Physical Activity in Overweight Individuals
Christoph Höchsmann, Michael Schüpbach, Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss
Sports Medicine.2016; 46(6): 845. CrossRef - Recruitment of older adults with type 2 diabetes into a community-based exercise and nutrition randomised controlled trial
Eliza G. Miller, Caryl A. Nowson, David W. Dunstan, Deborah A. Kerr, Vicky Solah, David Menzies, Robin M. Daly
Trials.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Sense of mastery as mediator buffering psychological distress among people with diabetes
Karin Elisabeth Bennetter, Jocelyne Clench–Aas, Ruth Kjærsti Raanaas
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(5): 839. CrossRef - Cardiorespiratory Exertion While Playing Video Game Exercises in Elderly Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Christoph Höchsmann, Nicole Zürcher, Andrea Stamm, Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss
Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine.2016; 26(4): 326. CrossRef - A Mixed Methods Study Exploring the Factors and Behaviors That Affect Glycemic Control Following a Structured Education Program
Dympna Casey, Mary Clare O’Hara, Ben Meehan, Molly Byrne, Sean F. Dinneen, Kathy Murphy
Journal of Mixed Methods Research.2016; 10(2): 182. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Perceived Therapeutic Efficacy Scale for Adhering to a Cholesterol-Lowering Diet
Yaguang Zheng, Lauren Terhorst, Jina Choo, Lora E. Burke
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2014; 29(3): 257. CrossRef - Change in Physical Activity after a Diabetes Diagnosis
Kristin L. Schneider, Christopher Andrews, Kathleen M. Hovey, Rebecca A. Seguin, Todd Manini, Michael J. LaMonte, Karen L. Margolis, Molly E. Waring, Yi Ning, Stacy Sims, Yunsheng Ma, Judith Ockene, Marcia L. Stefanick, Sherry L. Pagoto
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2014; 46(1): 84. CrossRef - Factors influencing self‐management in patients with type 2 diabetes: a quantitative systematic review protocol
Annamaria Bagnasco, Patrizia Di Giacomo, Roberta Da Rin Della Mora, Gianluca Catania, Carlo Turci, Gennaro Rocco, Loredana Sasso
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2014; 70(1): 187. CrossRef - Abnehmen beginnt im Kopf, nicht im Bauch
Christine Graf, Nina Ferrari, Stefanie Eiser
MMW - Fortschritte der Medizin.2013; 155(S1): 91. CrossRef - Moderate- and vigorous-intensity exercise behaviour according to the Transtheoretical Model: associations with smoking and BMI among Austrian adults
Franziska Großschädl, Sylvia Titze, Nathalie Burkert, Willibald J. Stronegger
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2013; 125(9-10): 270. CrossRef - Acute Exercise Induces FGF21 Expression in Mice and in Healthy Humans
Kook Hwan Kim, Seong Hun Kim, Young-Ki Min, Hun-Mo Yang, Jeong-Beom Lee, Myung-Shik Lee, Cedric Moro
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(5): e63517. CrossRef - Exercise for diabetic neuropathy: A toe in the therapeutic door
A. Gordon Smith, Robin Marcus
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2012; 26(5): 361. CrossRef
- Factors associated with diabetes mellitus among adults: Findings from the Indonesian Family Life Survey-5

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





